11 Useful terms and terminologies
Sometimes we can use words interchangeably which can cause confusion so below are some terms we use a lot in the team and what they mean and synonyms.
- NDORMS (Nuffield Department of Orthopaedics, Rheumatology and Musculoskeletal Sciences).
This is our department. NDORMS is part of the Medical Sciences Division of the University of Oxford.
- Botnar (Botnar Institute for Musculoskeletal Sciences)
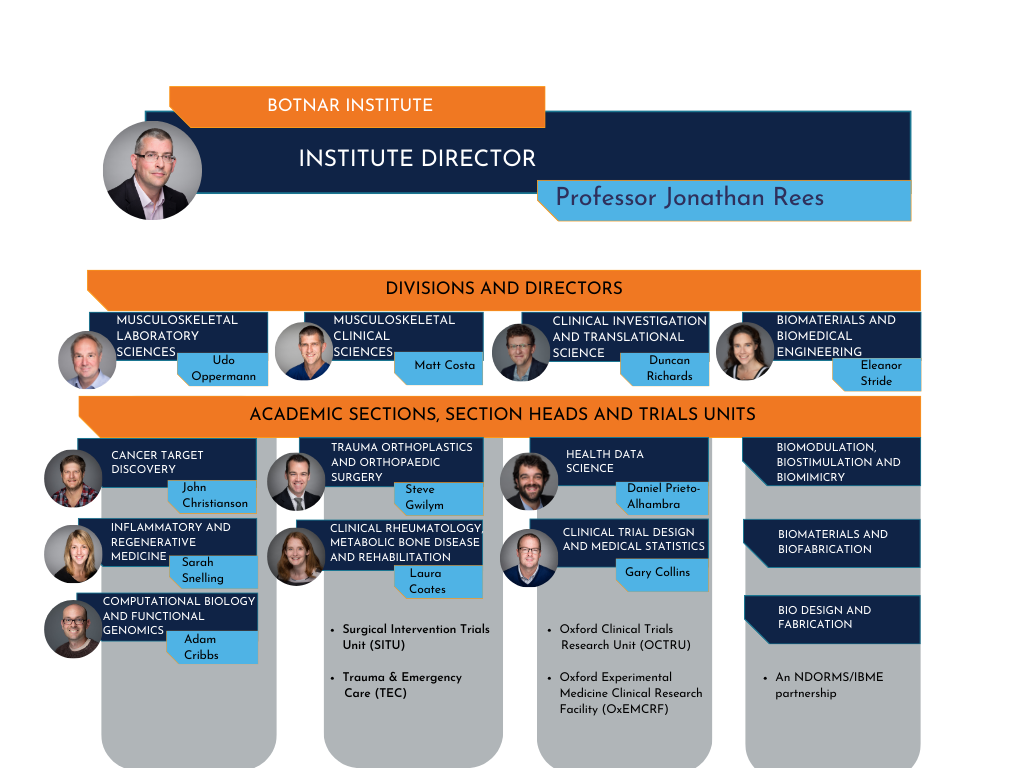
This is where you work (if you dont why are you reading this?!). The research work in the department (NDORMS) takes place across three world-leading research institutes: the Botnar Institute for Musculoskeletal Sciences, the Kennedy Institute for Rheumatology and the Kadoorie Centre.
- HDS (Health Data Sciences)
The Botnar Institute is structured into four academic divisions. From the divisions there are sections. We work under academic section Health Data Sciences.
- CSM (Centre for Statistics in Medicine)
The CSM is based at Botnar with an aim to advance healthcare practice and policy that changes lives, through excellent research. Our group is one of the teams as well as others apart of the CSM.
- CDM (Common Data Model)
A common data model is a standard that defines a common language. If people use this common language for their databases this means data can be harmonized. Think of it like a foreign plug adaptor, which turns data into one format. What this means is all databases are in the same format we can run the same code without writing bespoke code for each database we want to use for a study.
- OMOP (Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership)
OMOP CDM is an open community data standard, designed to standardize the structure and content of observational data and to enable efficient analyses that can produce reliable evidence. In simple terms it is a type of common data model people could use.
- OHDSI (Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics)
This is a program which is a global collaborative program to bring out the value of health data through large-scale analytics. Includes academia and industry. People in this collaboration use the OMOP CDM. More information here. Note: We lead the OHDSI UK hub.
- Data partner
This is the term we use for a database source usually this is a person/s responsible for executing the analytical code.
- Individual/patient level data
Patient level data. i.e for each patient all the information. We only have access to patient level data for our datasets based within the team. We never have access to patient level data from other data partners.
- Aggregated level data
As the name suggests the data only contains aggregated results such as results from a study. Aggregated data from data partners can be shared subject to the protocol and data sharing agreement with data partner.
- Federated network studies
When the same analytical code is run across multiple databases/data partners across the UK, Europe, Globe etc in one study. Note we only share analytical code with a data partner and they run the code we never have access to individual/patient level data.
- EHDEN (European Health Data Evidence Network)
This is a large consortium with 25 partners operating in Europe. Note We are apart of this consortium and have led and participated in various federated network studies. More information here here.
- DARWIN
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the European Medicines Regulatory Network established a coordination centre to provide timely and reliable evidence on the use, safety and effectiveness of medicines for human use, including vaccines, from real world healthcare databases across the European Union (EU). This capability is called the Data Analysis and Real World Interrogation Network (DARWIN EU®). Dani is a deputy director. Note We lead and participate in studies that are requested by EMA. Furthermore, we develop R code and packages that are used in this project. More information here.
- Instantiating
When you hear this term it basically means extracting and creating a table containing individuals with specified characteristics for example with a diagnosis of hypertension as a table in the database.